01. Benefits
Advantages and benefits of hydrogen
- Zero emission: the only emission from a fuel cell vehicle using hydrogen is water steam. Hydrogen is thus a clean fuel for cars without emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change.
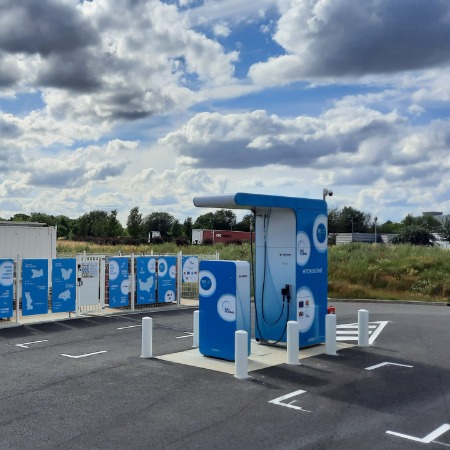
- Fast refuelling: hydrogen charging stations are quite similar to the traditional filling stations. As hydrogen vehicles don’t need to be plugged in to charge - unlike battery powered electric cars - the process of refuelling is quick.
- Long driving range: fuel-cell vehicles also have a longer range than battery powered electric cars. They now have a range of 500 to 800 km.