01. Definition
What is the energy crisis?
In recent years, many scientists have raised their voice to warn about climate change, caused notably by the burning of oil and coal in order to produce energy.
Solutions to the energy crisis
Over the last two centuries, energy needs have skyrocketed dramatically, especially because of the transportation and industry sectors. However, fossil fuel are polluting and their reserves are limited. We know today that these resources are close to exhaustion and our societies are facing a major challenge: the energy crisis.


01. Definition

02. Causes

03. Impacts

04. Solutions
05. Implementations
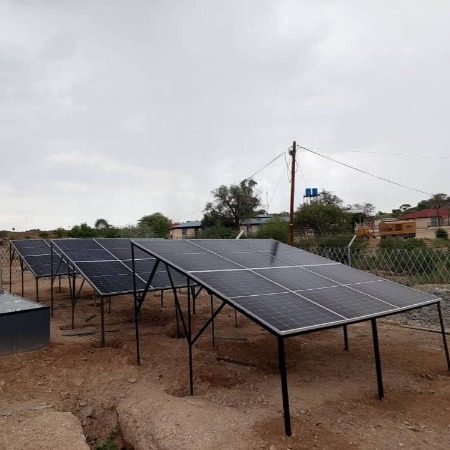
MPower Ventures by MPower Ventures implemented by Kamanjab Municipality in Kamanjab (Namibia) in 2024
Cooling as a Service by BASE implemented by Coop in Oslo (Norway) in 2021
Philéole by Phileole S. A. implemented by Foutaine Pajo /Lagoon in La Rochelle (France) in 2024
Philéole by Phileole S. A. implemented by Skypark Business Center, Luxembourg Airport in Luxembourg (Luxembourg) in 2025
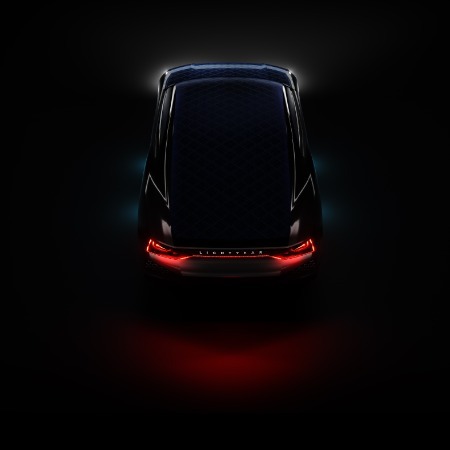
Lightyear One – Solar electric car by Lightyear implemented by BNP Paribas in Paris (France) in 2023
Helios Exchange by Helios Exchange, Inc. implemented by New York City in New York (United States) in 2019
Geothermal panel by Enerdrape implemented by Realstone in Lausanne (Switzerland) in 2021
Geothermal panel by Enerdrape implemented by Coop in Renens (Switzerland) in 2023
Geothermal panel by Enerdrape implemented by Next Immobilier SA in Aigle (Switzerland) in 2024
Geothermal panel by Enerdrape implemented by ENGIE in Paris (France) in 2025
CONTAINWATT by monkilowatt implemented by Médecins Sans Frontières in Ouaddaï (Chad) in 2024
Eco Touch by OGGA implemented by OGGA in Meulan-en-Yvelines (France) in 2020
Hivenet by Hivenet implemented by Inria (French National Institute for Research in Digital Science and Technology) in Le Chesnay Cedex (France) in 2022
Hamwells Blue by Hamwells implemented by The Green Village, Woon Friesland, Bouwgroep Dijkstra Draaisma, Bewonersraad Friesland in Delft (Netherlands) in 2021
Hamwells Blue by Hamwells implemented by Megaplex in Rotterdam (Netherlands) in 2023
Hamwells Blue by Hamwells implemented by The New Makers in Delft (Netherlands) in 2025

06. Conclusion