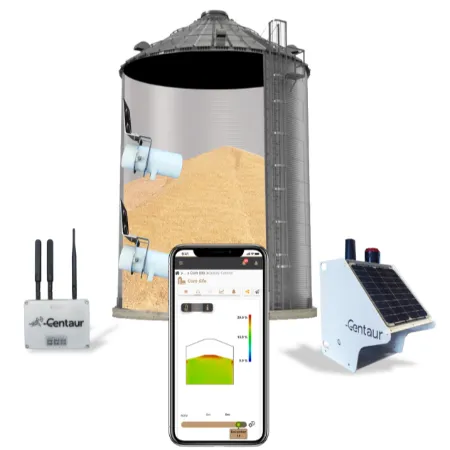
01. Benefits
Sustainable agriculture advantages
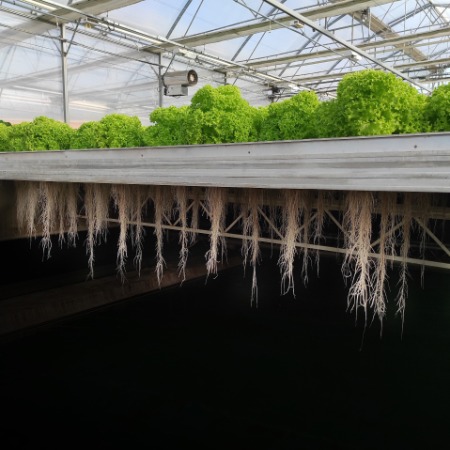
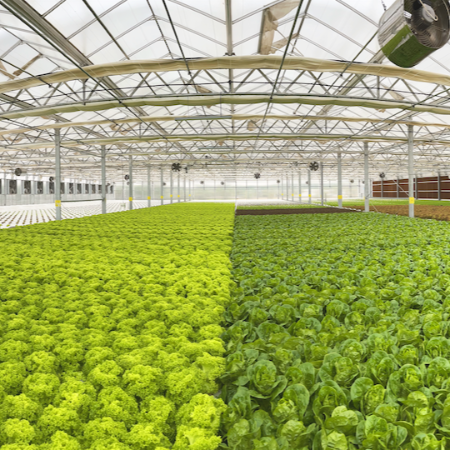
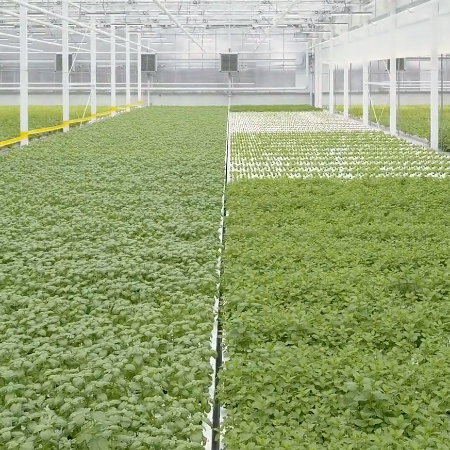
- Environmental protection: the first advantage of sustainable agriculture is the protection of the environment, reducing erosion and natural resource degradation, improving air and water quality, increasing biodiversity, as well as decreasing carbon emissions.
- Public health improvement: sustainable agriculture don’t use hazardous pesticides and fertilizers. As a result, farmers are able to produce safer and healthier food for consumers and surrounding communities.
- Economic and social equity: another benefit of sustainable farming methods is that they provide decent income, but also jobs, food and other goods and services for the majority of people now living in poverty. Besides, it allows to boost rural territories and create social links between the rural and urban world.