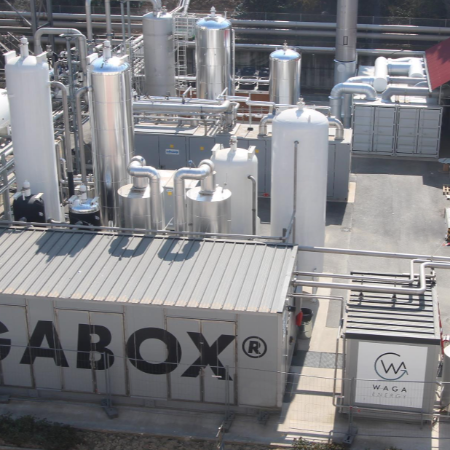
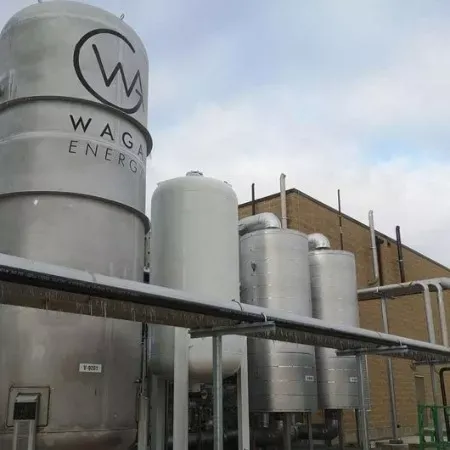
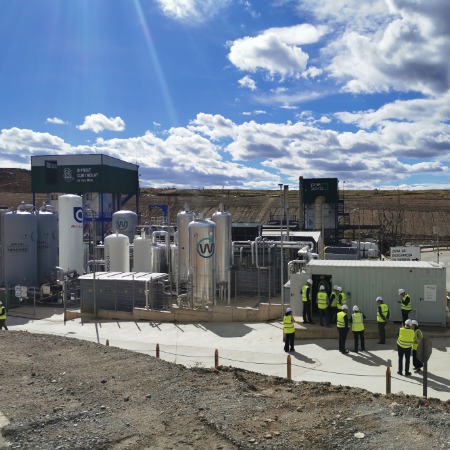
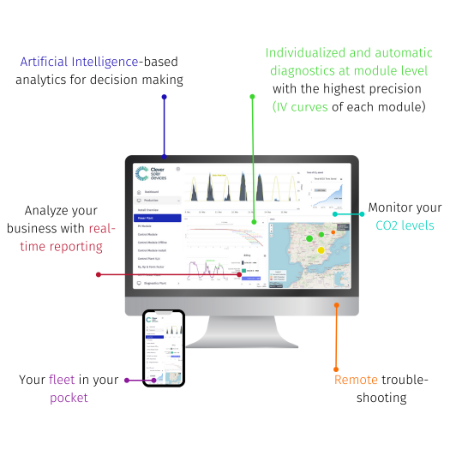
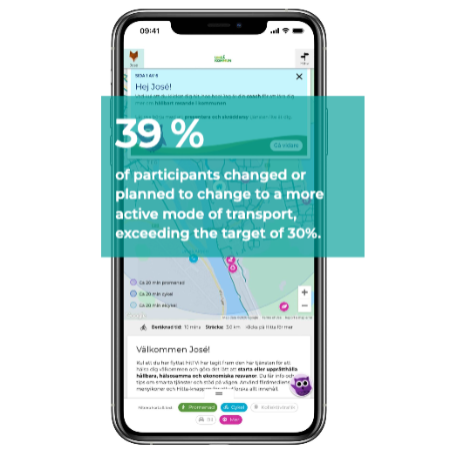
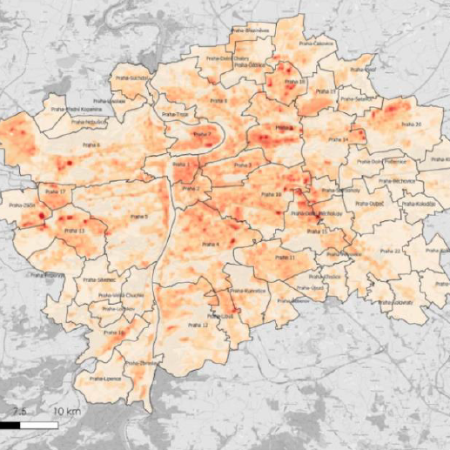
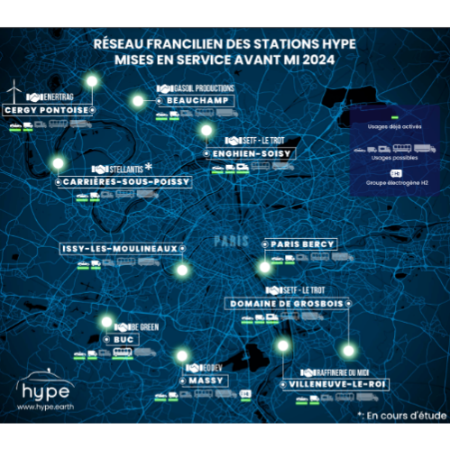
01. Definition
What is air pollution?
- Local: this concerns the quality of ambient air within a radius of a few kilometers
- Regional: pollution like acid rain, photochemical reactions and degradation of water quality at distances of a few kilometers to a thousand kilometers
- Global: depletion of the ozone layer and global warming caused by the emission of greenhouse gases, mainly carbon dioxide (CO2)