01. Definition
What is global warming?
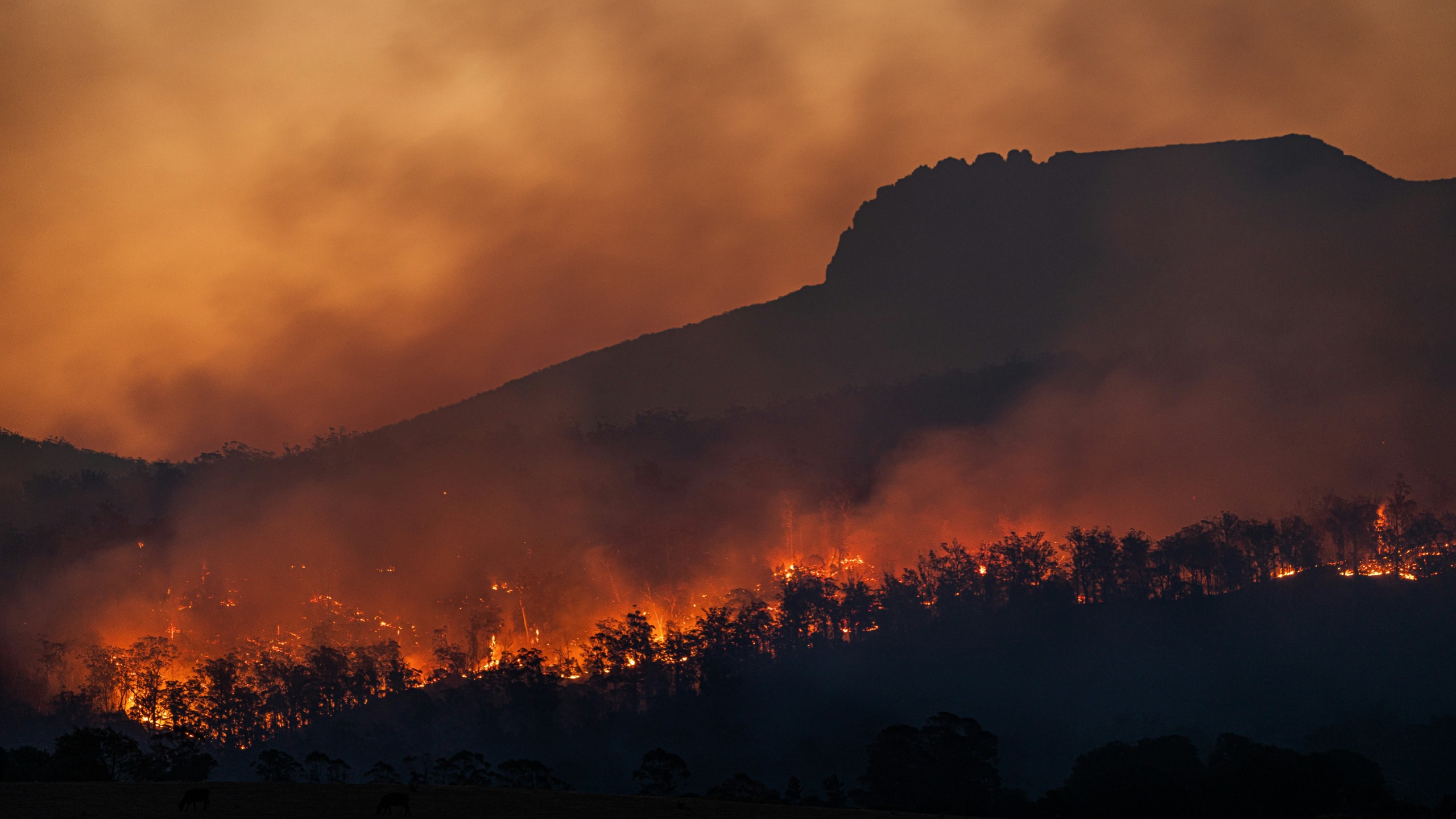
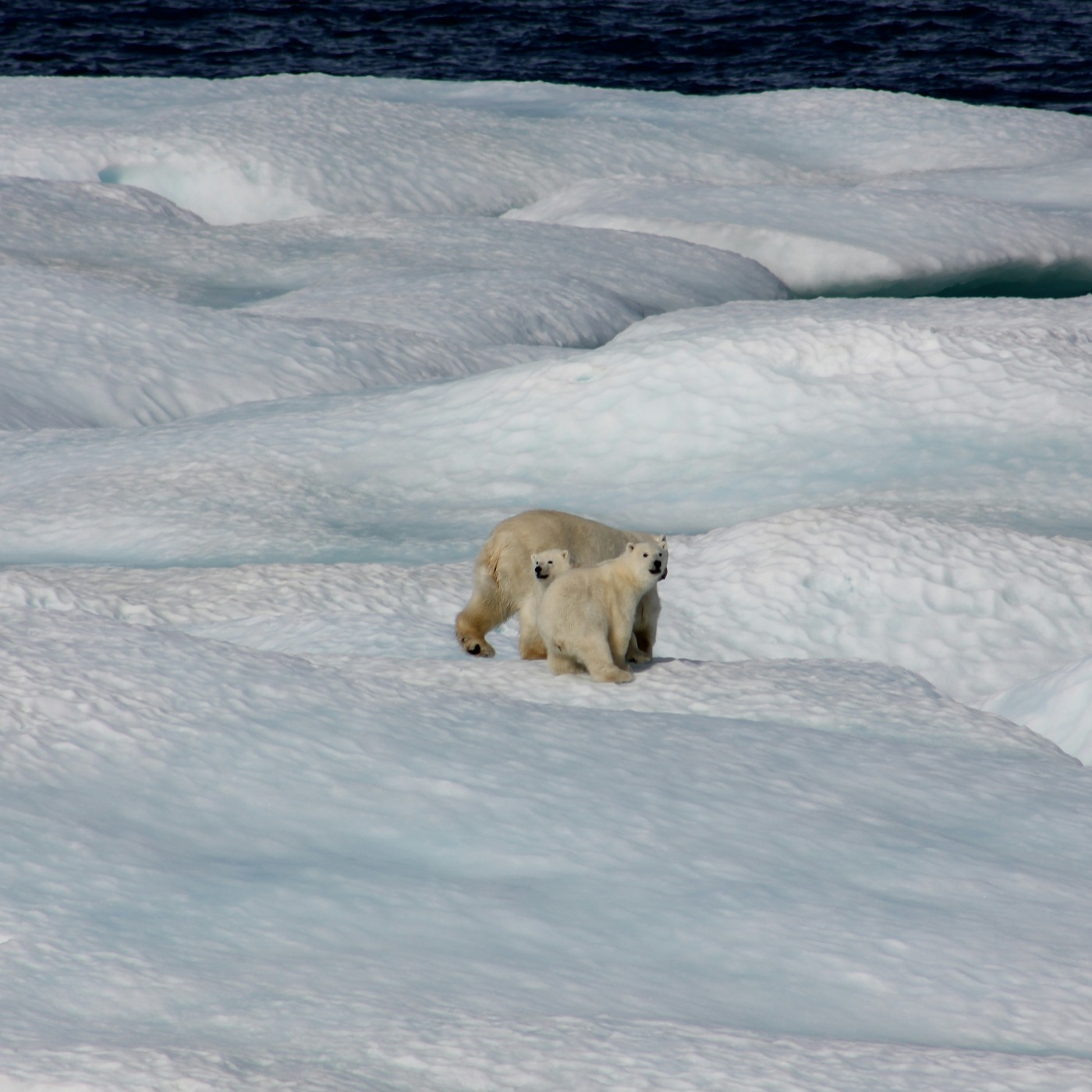
In fact, the average temperature of the planet has increased by 0.8º Celsius (33.4° Fahrenheit) compared to the end of the 19th century. Each of the last three decades has been warmer than all previous decades since the beginning of the statistical surveys in 1850.
At the pace of current CO2 emissions, scientists expect an increase of between 1.5° and 5.3°C (34.7° to 41.5°F) in average temperature by 2100. If no action is taken, it would have harmful consequences to humanity and the biosphere.