01. Definition
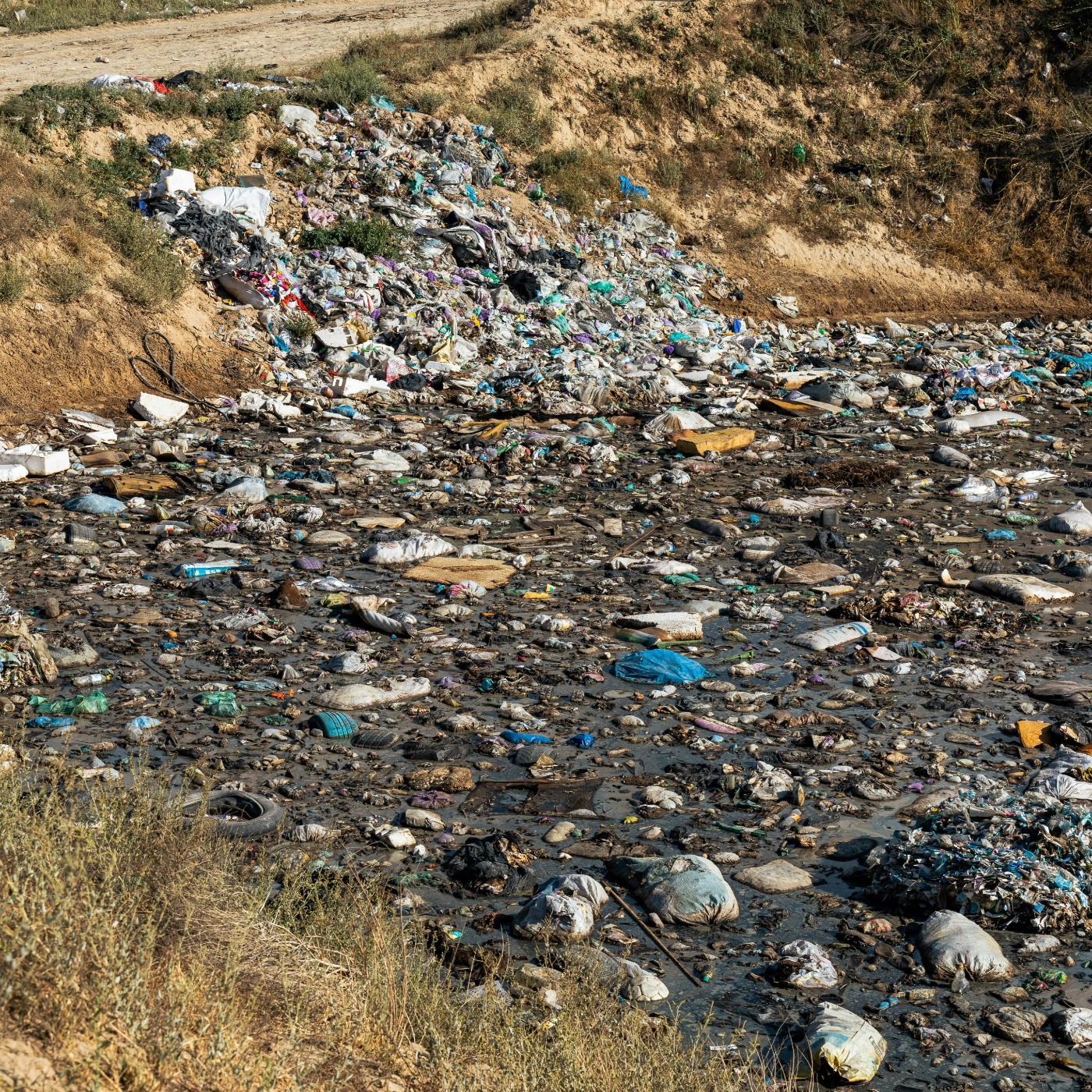
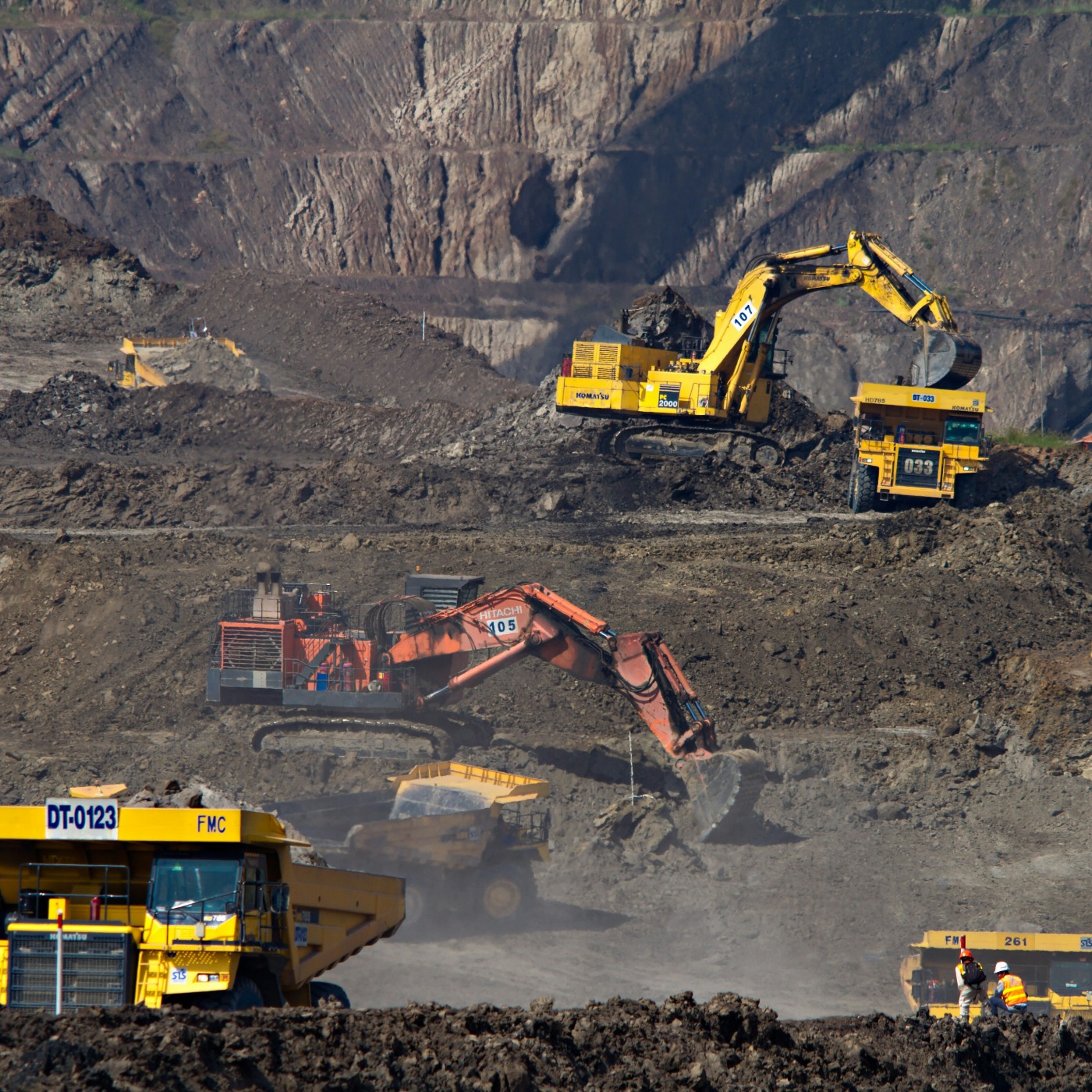
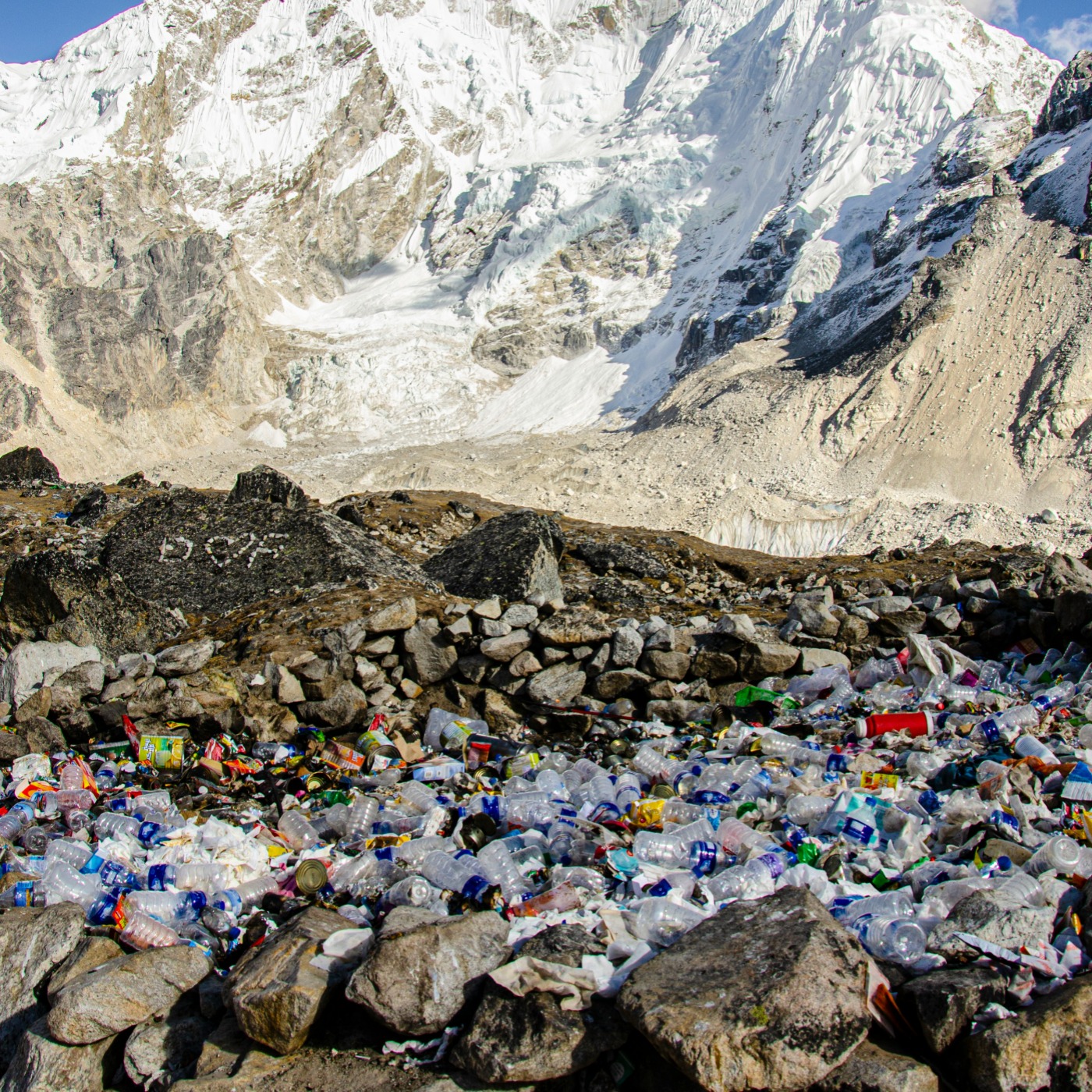
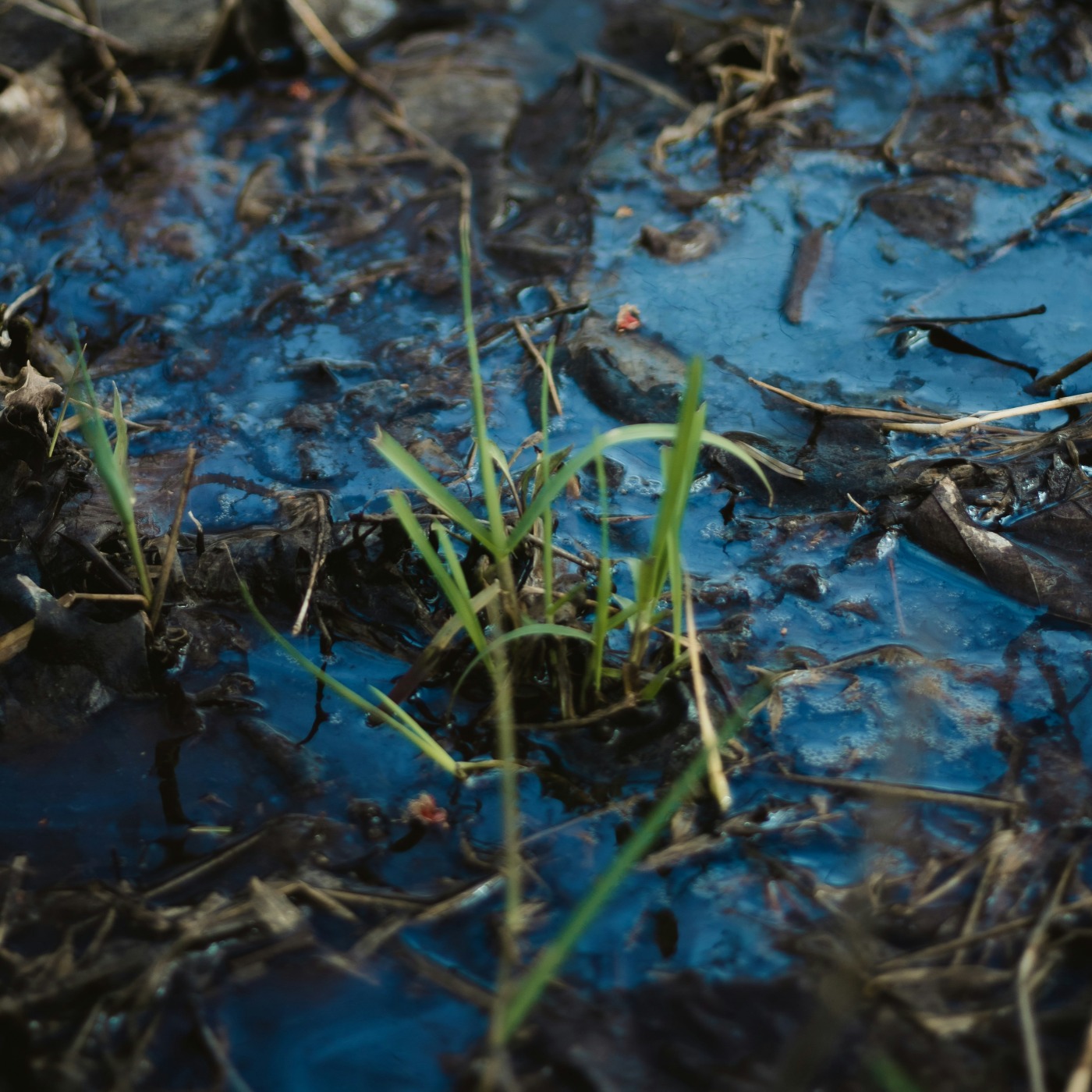
What is land pollution?
A soil is polluted when it contains an abnormal concentration of chemical compounds potentially dangerous to human health, plants or animals.
There are different types of land pollution:
- Agricultural land pollution
- Chemicals
- Solid waste