01. Definition
Solutions to water scarcity
Tackling Water Scarcity: Understanding the Challenges and Solutions
Water scarcity is not just an environmental issue; it’s a global crisis impacting millions of lives daily. As the demand for water continues to outstrip supply, the effects are being felt from the smallest communities to the largest cities. It’s a challenge.



02. Causes
The Root Causes of Water Scarcity
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns, reduced glacial runoff, and more frequent droughts are making water less predictable and harder to manage.
- Growing Population: As the global population swells, so too does the demand for water, putting immense pressure on already stressed resources.
- Inefficient Water Management: Poorly managed water systems, from leaky infrastructure to wasteful agricultural practices, exacerbate the scarcity problem.
- Pollution: Contaminated water sources further limit the availability of safe drinking water, adding another layer of complexity to the issue.
03. Impacts
The Far-Reaching Impacts
- Health Risks: Without access to clean water, diseases like cholera and typhoid thrive, particularly in regions already struggling with poverty.
- Threat to Food Security:Agriculture, which consumes the majority of the world’s freshwater, is hit hard by water shortages, leading to reduced crop yields and higher food prices.
- Economic Disruption: Industries reliant on water face production challenges, potentially leading to job losses and economic instability.
- Social and Political Tensions: When water is scarce, competition can lead to conflicts, both within and between nations.

04. Solutions
Water scarcity solutions
05. Implementations
Success Stories

Drop2Drink Unit by D2D Water Solutions B.V. implemented by De Watergroep in Schaarbeek (Belgium) in 2024

WaterFlush by EcoNeves implemented by Hôpital Necker Paris in Paris (France) in 2018

Shayp by Shayp implemented by Professional High School Le Balcon des Ardennes in Saint-Laurent (France) in 2021

Hydraloop by Hydraloop Systems BV implemented by Upgrade Real Estate in Ghent (Belgium) in 2022

Hydraloop by Hydraloop Systems BV implemented by Wind Groep in Lemmer (Netherlands) in 2023

Hydraloop by Hydraloop Systems BV implemented by Intercontinental Hotel Group: IHG Voco™ in Vilvoorde (Belgium) in 2023

OSMOSUN by OSMOSUN implemented by Island of Santiago in Island of Santiago (Cape Verde) in 2021
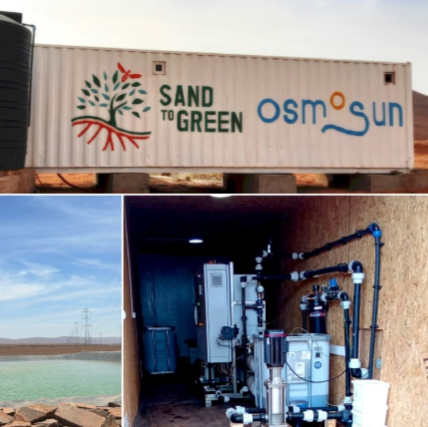

OSMOSUN by OSMOSUN implemented by Sand to Green in the Guelmim-Oued Noun region (Morocco) in 2024
The SunAir Fountain® by AGUA DE SOL implemented by 2D Water in Marrakesh (Morocco) in 2024
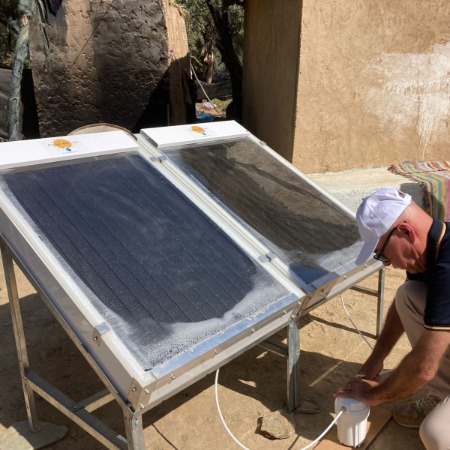

The SunAir Fountain® by AGUA DE SOL implemented by Amal Biladi Association in Aït Bourd (Morocco) in 2024
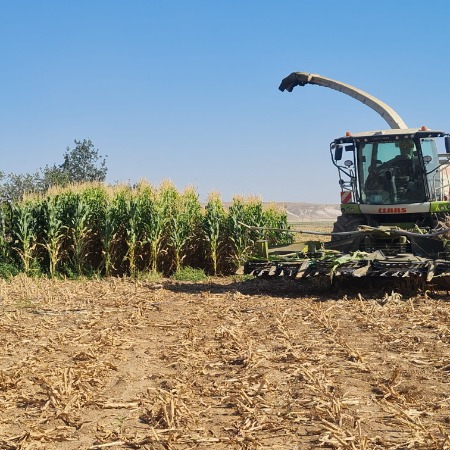

From the Ground to the Cloud by RAINCATCHER implemented by TİGEM in Konya (Turkey) in 2025

From the Ground to the Cloud by RAINCATCHER implemented by Mistikoğlu Tarım Farm in Hatay (Turkey) in 2025

AQS Aquarius Spectrum by AQS (Aquarius Spectrum) implemented by A2A Ciclo Idrico in Brescia (Italy) in 2020
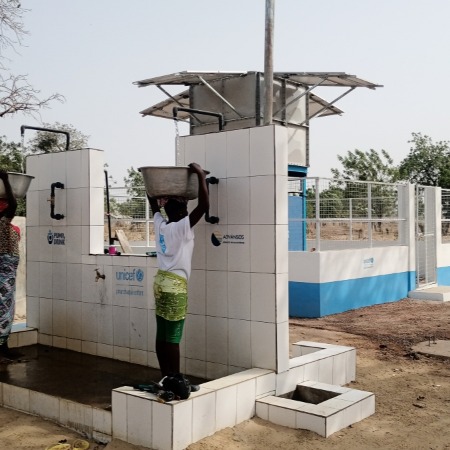

Pump&Drink by Sotrad Water implemented by Ministère de l'Eau et de l'Hydraulique Villageoise + UNICEF in Dapaong (Togo) in 2022

Waterless Urinal by URIMAT Schweiz AG implemented by McDonald's in Zurich (Switzerland) in 2002

Hummbox Smart watering by Simpliciti implemented by Municipality of Martigues in Martigues (France) in 2022

06. Challenges
Overcoming the Challenges
- Financial Barriers: Many regions struggle with the funding needed to upgrade water infrastructure and implement new technologies.
- Political Hurdles: Effective water management requires strong political will, which can be hard to come by in areas of instability.
- Cultural Resistance: Sometimes, traditional practices and beliefs can slow the adoption of new water-saving technologies.
- Unpredictable Climate: As climate patterns continue to shift, planning for water management becomes increasingly complex.

07. Conclusion








